Ceng 328 Operating Systems
Final
June 1, 2010 15.00-17.00
Good Luck!
You are allowed to use CALCULATOR.
No any other electronic equipment is allowed.
Answer all the questions.
- (15 pts)
- i
- What is time sharing?
- ii
- Describe the concept of the multiprogramming level.
- iii
- What is meant by the term context switch? What might cause a context switch to occur?
- (40 pts) Choose only four questions.
- iv
- Explain why an operating system can be viewed as a resource allocator.
- v
- Describe the difference between the
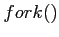 and
and 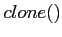 Linux system calls.
Linux system calls.
- vi
- 1
- What is a race condition?
- 2
- Suppose that we have a message-passing system using mailboxes. When sending to a full mailbox or trying to receive from an empty one, a process does not block. Instead, it gets an error code back. The process responds to the error code by just trying again, over and over, until it succeeds. Does this scheme lead to race conditions?
- vii
- Describe the dining-philosophers problem and how it relates to operating systems.
- viii
- For deadlock to occur, four conditions must hold: mutual exclusion, hold and wait, no preemption, and circular wait. If any one condition does not hold, no deadlock can occur. Assume we want to allow preemption , and thus get out of deadlocks; in other words, if a deadlock is detected, we will forcibly take a lock away from a thread; by repeatedly doing this, we will eventually undo the deadlock. What new problems are introduced by this preemptive approach?
- ix
- What causes a page fault? What actions may be taken by the operating system when servicing a page fault?
- x
- Describe internal and external fragmentation and explain the difference between them. Which one(s) occurs in paging systems? Which one(s) occurs in systems using pure segmentation?
- (15 pts) Explain the UNIX index node (inode) structure in detail.
- (20 pts) Consider the following sets of processes, with the length of the CPU-burst time given in milliseconds. Arrival time is the time at which the process is added to the ready queue in the order P1, P2, P3, P4, P5.
| Process |
Burst Time |
Priority |
Arrival Time |
|---|
| P1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
| P2 |
2 |
3 |
0 |
| P3 |
8 |
3 |
0 |
| P4 |
1 |
4 |
0 |
| P5 |
5 |
2 |
0 |
A smaller priority number implies a higher priority. Scheduling algorithms:
- Round Robin (RR); assume that the system is multiprogrammed, and that each job gets its fair share of the CPU.
- Priority Scheduling (PS); assume that only one job at a time runs, until it finishes.
- First Come First Served (FCFS); assume that only one job at a time runs, until it finishes.
- xi
- Draw appropriate charts illustrating the execution of these processes using RR, PS, FCFS. Ignore process switching overhead.
- xii
- Calculate the wait (W) and turnaround (T) times of each process for each strategy. Also calculate the average wait and turnaround times under each strategy. Fill the table below
|
|
RR |
RR |
PS |
PS |
FCFS |
FCFS |
|---|
|
|
W |
T |
W |
T |
W |
T |
|
Process |
Time |
Time |
Time |
Time |
Time |
Time |
|---|
|
P1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
P6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Average |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- xiii
- Discuss which strategy is the best according to the table.
- (20 pts) Estimated total average access time in disks is given as the following formula
The following values are given;
Average Seek Time: 2 ms.
6000 rpm (rpm: revolution per minute).
A millisecond (ms) is a thousandth (1/1000) of a second.
Sectors per Track: 64.
Logical Block Size: 512 bytes.
File Size: 20972032 bytes.
- xiv
- Describe each term in the formula.
- xv
- Fill the table for the file stored compactly (adjacent tracks).
- xvi
- Fill the table for the file sectors distributed randomly over the disk.
- (10 pts) What is ``Mutual Exclusion''? Describe the ``Strict Alternation'' as a solution for mutual exclusion (see the figure)?
Figure 1:
Strict alternation for achieving mutual exclusion, (a) process0 (b) process1.
|
|
Cem Ozdogan
2010-06-02