



Next: Initializing Semaphores
Up: Processes Semaphores
Previous: Processes Semaphores
Contents
- The calls semget and semctl allocate and deallocate semaphores, which is analogous to shmget and shmctl for shared memory. Invoke semget with:
- a key specifying a semaphore set,
- the number of semaphores in the set,
- permission flags as for shmget
- The return value is a semaphore set identifier. You can obtain the identifier of an existing semaphore set by specifying the right key value.
- Semaphores continue to exist even after all processes using them have terminated. The last process to use a semaphore set must explicitly remove it. To do so, invoke semctl with
- the semaphore identifier,
- the number of semaphores in the set,
- IPC_RMID as the third argument,
- any union semun value as the fourth argument (which is ignored).
- Unlike shared memory segments, removing a semaphore set causes Linux to deallocate immediately.
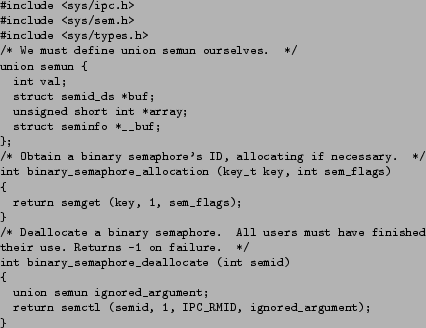
- The following http://siber.cankaya.edu.tr/SystemsProgramming/cfiles/sem_all_deall.ccode (see Fig. 6.2.1) presents functions to allocate and deallocate a binary semaphore.
Figure 6.2:
Allocating and Deallocating a Binary Semaphore
 |




Next: Initializing Semaphores
Up: Processes Semaphores
Previous: Processes Semaphores
Contents
Cem Ozdogan
2007-05-16
