



Next: Multistage Networks
Up: Switch-Based Interconnection Networks
Previous: Crossbar Networks
Contents
Single-Stage Networks
Figure 2.4:
The different settings of the
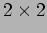 SE.
SE.
|
|
- In this case, a single stage of switching elements (SEs) exists between the inputs and the outputs of the network.
- The simplest switching element that can be used is the
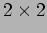 switching element (SE). Figure 2.4 illustrates the four possible settings that an SE can assume.
switching element (SE). Figure 2.4 illustrates the four possible settings that an SE can assume.
- Straight; the upper input is transferred to the upper output and the lower input is transferred to the lower output.
- Exchange; the upper input is transferred to the lower output and the lower input is transferred to the upper output.
- Upper-broadcast; the upper input is broadcast to both the upper and the lower outputs.
- Lower-broadcast; the lower input is broadcast to both the upper and the lower outputs.
- To establish communication between a given input (source) to a given output (destination), data has to be circulated a number of times around the network.
- A well-known connection pattern for interconnecting the inputs and the outputs of a single-stage network is the Shuffle-Exchange.
- Two operations are used.
- Shuffle;
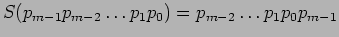
- Exchange;
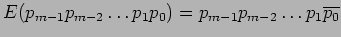
With shuffle (S) and exchange (E) operations, data is circulated from input to output until it reaches its destination.
- If the number of inputs, for example, processors, in a single-stage IN is N and the number of outputs, for example, memories, is N, the number of SEs in a stage is N/2. The maximum length of a path from an input to an output in the network, measured by the number of SEs along the path, is
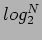 .
.
- Example: In an 8-input single stage Shuffle-Exchange if the source is
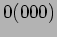 and the destination is
and the destination is 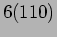 , then the following is the required sequence of Shuffle/ Exchange operations and circulation of data:
The network complexity of the single-stage interconnection network is
, then the following is the required sequence of Shuffle/ Exchange operations and circulation of data:
The network complexity of the single-stage interconnection network is 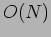 and the time complexity is
and the time complexity is 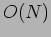 .
.
- In addition to the shuffle and the exchange functions, there exist a number of other interconnection patterns that are used in forming the interconnections among stages in interconnection networks. Among these are the Cube and the Plus-Minus
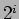 (PM2I) networks.
(PM2I) networks.




Next: Multistage Networks
Up: Switch-Based Interconnection Networks
Previous: Crossbar Networks
Contents
Cem Ozdogan
2006-12-27
![\includegraphics[scale=0.6]{figures/singlestagesettings.ps}](img53.png)