


Next: About this document ...
Ceng 471 & Ceng 505 Parallel Computing
Final
Jan 27, 2009 17.30-19.30
Good Luck!
1 (40 Pts) Summation of numbers is performed both in serial and parallel ways. For parallel computation, the environment is the networked workstations and the sequential computation is also done in the same cluster. The following table is obtained;
| TIME |
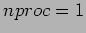 |
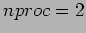 |
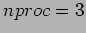 |
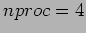 |
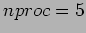 |
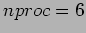 |
|
| 100 |
0.013541 |
0.015713 |
0.015420 |
0.017393 |
0.018216 |
0.025741 |
|
| 200 |
0.018175 |
0.018387 |
0.019951 |
0.022900 |
0.026010 |
0.030067 |
|
| 500 |
0.036738 |
0.027887 |
0.032696 |
0.041647 |
0.433383 |
0.049059 |
|
| 1000 |
0.072881 |
0.047775 |
0.060789 |
0.093839 |
0.097799 |
0.113722 |
|
| 2000 |
0.145120 |
0.078808 |
0.111233 |
0.188817 |
0.143317 |
0.211288 |
|
| 5000 |
0.365731 |
0.197714 |
0.269206 |
0.313151 |
0.371891 |
0.347993 |
|
| 10000 |
0.749948 |
0.390106 |
0.507074 |
0.636745 |
0.665334 |
0.705855 |
|
| 20000 |
1.571937 |
0.865633 |
1.086707 |
1.225067 |
1.273847 |
1.338983 |
|
- i
- Complete the following tables.
| Speed-Up |
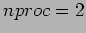 |
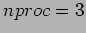 |
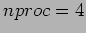 |
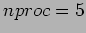 |
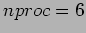 |
|
| 100 |
0.86 |
0.88 |
0.78 |
|
|
|
| 200 |
0.99 |
0.91 |
0.79 |
|
|
|
| 500 |
1.32 |
1.12 |
0.88 |
|
|
|
| 1000 |
1.53 |
1.2 |
0.78 |
|
|
|
| 2000 |
1.84 |
1.3 |
0.77 |
|
|
|
| 5000 |
1.85 |
1.36 |
1.17 |
|
|
|
| 10000 |
1.92 |
1.48 |
1.18 |
|
|
|
| 20000 |
1.82 |
1.45 |
1.28 |
|
|
|
| Efficiency |
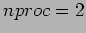 |
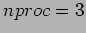 |
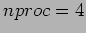 |
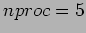 |
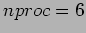 |
|
| 100 |
0.43 |
0.29 |
0.19 |
|
|
|
| 200 |
0.49 |
0.3 |
0.2 |
|
|
|
| 500 |
0.66 |
0.37 |
0.22 |
|
|
|
| 1000 |
0.76 |
0.4 |
0.19 |
|
|
|
| 2000 |
0.92 |
0.43 |
0.19 |
|
|
|
| 5000 |
0.92 |
0.45 |
0.29 |
|
|
|
| 10000 |
0.96 |
0.49 |
0.29 |
|
|
|
| 20000 |
0.91 |
0.48 |
0.32 |
|
|
|
- ii
- Analyze the tables in detail.
- iii
- How many processor should be used for a specific value of
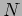 ? Why?
? Why?
- iv
- Given the following table. The values are found as
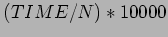
| N |
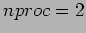 |
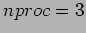 |
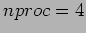 |
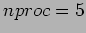 |
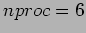 |
|
| 100 |
1.571300 |
1.542000 |
1.739300 |
1.821600 |
2.574100 |
|
| 200 |
0.919350 |
0.997550 |
1.145000 |
1.300500 |
1.503350 |
|
| 500 |
0.557740 |
0.653920 |
0.832940 |
8.667660 |
0.981180 |
|
| 1000 |
0.477750 |
0.607890 |
0.938390 |
0.977990 |
1.137220 |
|
| 2000 |
0.394040 |
0.556165 |
0.944085 |
0.716585 |
1.056440 |
|
| 5000 |
0.395428 |
0.538412 |
0.626302 |
0.743782 |
0.695986 |
|
| 10000 |
0.390106 |
0.507074 |
0.636745 |
0.665334 |
0.705855 |
|
| 20000 |
0.432817 |
0.543354 |
0.612534 |
0.636924 |
0.669492 |
|
Can we estimate the 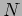 value(s) for each column that communication time overheads computation time?
value(s) for each column that communication time overheads computation time?
2 (30 Pts) Answer the following questions, choose only 5 of them.
- v
- Describe the Flynn's classification for computers. Which type of the computer we have made use of?
- vi
- Is it possible to have a system efficiency (E) of greater than %100? Discuss.
- vii
- Describe Blocking and Nonblocking Message-Passing.
- viii
- Compare the point-to-point and collective communications.
- ix
- What is embarrassingly parallel computations? Explain by an example.
- x
- What is the data parallel computations? Example it.
- xi
- Describe load balancing.
- xii
- What could be your criteria to choose a shared- or distributed-memory programming technique.
- xiii
- What is the difference between SIMD and SPMD models?
- xiv
- What are the main advantages of the compute clusters (Beowulf clusters)?
- xv
- Discuss the concept of communication overhead.
3 (30 Pts) Discuss the parallel programming/computing aspects of your presentation topic.



Next: About this document ...
Cem Ozdogan
2009-01-31