- The probability of the random variable
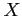 assuming a value between
assuming a value between 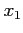 and
and 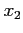 .
.
- The area under the curve between any two ordinates must also depend on the values
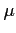 and
and 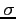 .
.
Figure 6:
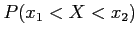 : area of the shaded region.
: area of the shaded region.
|
|
Figure 7:
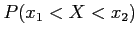 for different normal curves.
for different normal curves.
|
|
- Definition 6.1:

- Transformation:
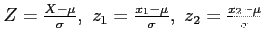
- Then;
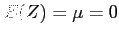 and
and
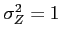
Figure 8:
The original and transformed normal distributions.
|
|
Example 6.2: Given a standard normal distribution, find the area under the curve that lies
- iii
- to the right of
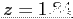
1 minus the area to the left of 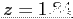 (see Table A.3)
(see Table A.3)
- iv
- between
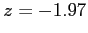 and
and 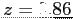
The area to the left of 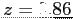 minus the left of
minus the left of 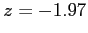
Figure 9:
Areas for Example 6.2.
|
|
Example 6.3:
Given a standard normal distribution, find the value of k such that
- v
-
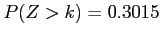
- vi
-
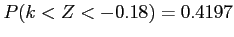
Figure 10:
Areas for Example 6.3.
|
|
- Example 6.4: Given a random variable
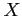 having a normal distribution with
having a normal distribution with 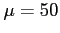 and
and
 ,
,
- Find the probability that
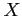 assumes a value between 45 and 62.
assumes a value between 45 and 62.
- Solution:
Figure 11:
Area for Example 6.4.
|
|
- Example 6.5 Given that a normal distribution with
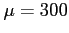 and
and
 , find the probability that
, find the probability that 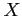 assumes a value greater than 362.
assumes a value greater than 362.
- Solution:
Figure 12:
Area for Example 6.5.
|
|
- Using the Normal Curve in Reverse
- We might want to find the value of
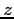 corresponding to a specified probability.
corresponding to a specified probability.
- The steps:
- Begin with a known area or probability.
- Find the
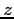 values corresponding to the tabular probability that comes closest to the specified probability.
values corresponding to the tabular probability that comes closest to the specified probability.
- Determine
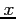 by rearranging the formula
by rearranging the formula
Example 6.6: Given a normal distribution with 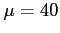 and
and 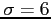 , find the value of
, find the value of 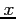 that has
that has
- vii
- 45% of the area to the left
From Table A.3 we find
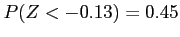 . Hence
. Hence
- viii
- 14% of the are to the right
From Table A.3, we find
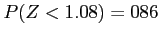 . Hence
. Hence
Figure 13:
Areas for Example 6.6.
|
|
Cem Ozdogan
2010-04-21
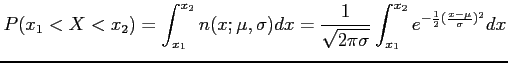

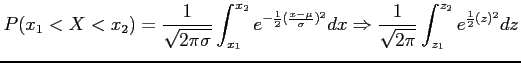
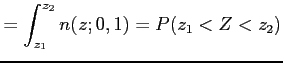
![]() (see Table A.3)
(see Table A.3)
![]() minus the left of
minus the left of ![]()
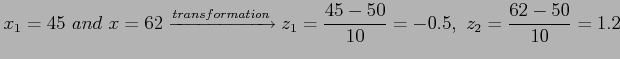
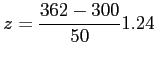
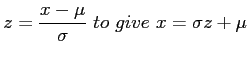
![]() and
and ![]() , find the value of
, find the value of ![]() that has
that has
![]() . Hence
. Hence
![]() . Hence
. Hence