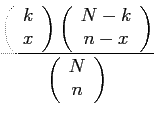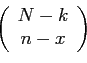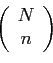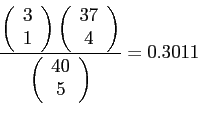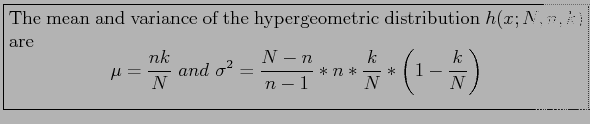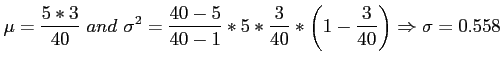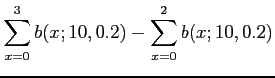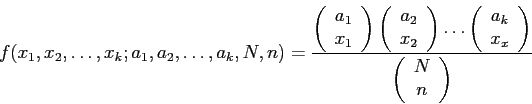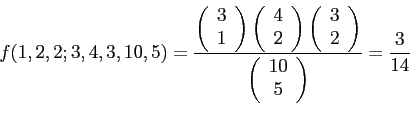- There are two types of sampling methods from a finite population. If the population is infinite, two methods do not make any difference.
- Binomial distribution: the sampling with replacement (
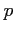 is constant)
is constant)
- Hypergeometric distribution: the sampling without replacement (
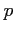 is not constant)
is not constant)
- Hypergeometric experiment:
- A random sample of size
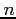 is selected without replacement from
is selected without replacement from 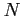 items.
items.
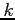 of the
of the 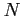 items may be classified as successes and
items may be classified as successes and 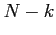 as failures.
as failures.
- Hypergeometric random variable: the number
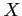 of successes of a hypergeometric experiment.
of successes of a hypergeometric experiment.
- The probability distribution of the hypergeometric variable
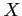 , the number of successes in a random sample of size
, the number of successes in a random sample of size 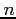 selected from
selected from 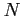 items of which
items of which 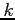 are labeled success and
are labeled success and 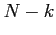 labeled failure;
labeled failure;
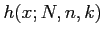 .
.
- the number of ways of selecting
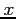 successes
successes
- the number of ways of selecting
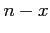 failures
failures
- the total number of samples of size
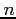 chosen from
chosen from 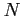 items
items
- Example 5.12: Lots of 40 components each are called unacceptable if they contain as many as 3 defective or more.
- The procedure for sampling the lot is to select 5 components at random and to reject the lot if a defective is found.
- What is the probability that exactly 1 defective is found in the sample if there are 3 defectives in the entire lot?
- Solution: Using hypergeometric distribution with
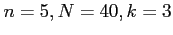 and
and  ;
;
- So this plan is likely not desirable since it detects a bad lot (3 defectives) only about 30% of the time.
- Theorem 5.3:
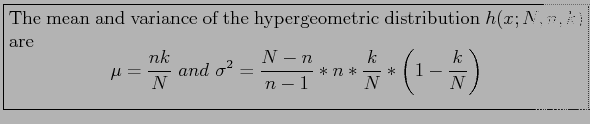
- Example 5.14:Find the mean and variance of the random variable of Example 5.12 (
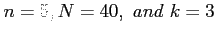 ) and then use Chebyshev's theorem to interpret the interval
) and then use Chebyshev's theorem to interpret the interval
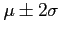
- Solution:
it has a probability of at least 3/ 4 of falling between -0.741 and 1.491.
- That is, at least three fourths of the time, the 5 components include less than 2 defectives.
- Relationship to the Binomial Distribution. If
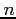 is small compared to
is small compared to 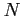 , the nature of the
, the nature of the 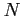 items changes very little in each draw. (when
items changes very little in each draw. (when
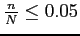 )
)
-
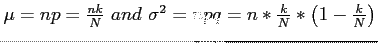 , where
, where
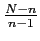 is negligible when
is negligible when 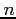 is smallrelative to
is smallrelative to 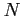 .
.
- The binomial distribution may be viewed as a large population edition of the hypergeometric distributions.
- Example 5.15: A manufacture of automobile tires reports that among a shipment of 5000 sent to a local distributor, 1000 are slightly faulty.
- If one purchases 10 of these tires at random from the distributor, what is the probability that exactly 3 are faulty?
- Solution:
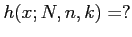
- Example 5.16: A group of 10 individuals are used for a biological case study.
- The group contains 3 people with blood type O, 4 with blood type A, and 3 with blood type B.
- What is the probability that a random sample of 5 will contain 1 person with blood type O, 2 with blood type A, and 2 with blood type B?
- Solution:
Cem Ozdogan
2010-04-08